Trochanteric bursitis occurs on the lateral aspect of the hip and can be a source of significant hip and thigh pain.

Trochanteric Bursitis
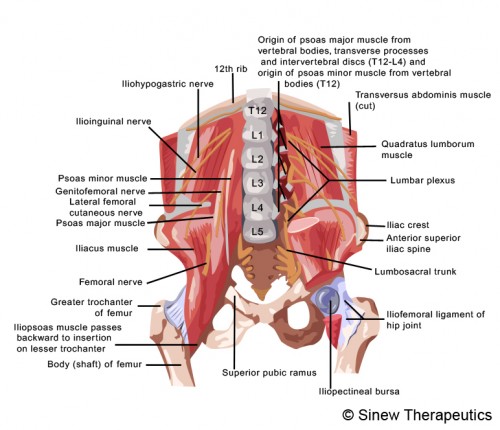
Anatomy Of The Greater Trochanter And Bursa
Bursae are cushion-like sacs that secrete a small amount of lubricating fluid. These sacs are located most anywhere that the surface of a muscle, tendon, ligament or skin rubs across the surface of a bone. The bursae are situated between these soft tissues and the hard bone, thereby reducing friction and wear and tear of the soft tissues. There isn’t a set number of bursae in the human body, as additional bursae often form anywhere that friction takes place between soft tissue and bone.
Some studies have shown over twenty bursae in the hip. However, there are three main bursae in the trochanteric area of the hip.
1. Trochanteric bursa - located between the gluteal muscle attachments and the greater trochanter on the outside of the hip.
2. Iliopsoas bursa - located at the front of the hip joint by the iliopsoas muscle.
3. Gluteus medius bursa - located between the greater trochanter and gluteus medius muscle. This bursa is located medial to the trochanteric bursa.
Of these, the trochanteric bursa is most prone to bursitis.
The greater trochanter is the bulky protrusion that makes up the upper lateral aspect of the femur (thigh bone). It is the bony bit that can be felt on the side of each hip. The greater trochanter is the attachment point for a number of muscles, such as the piriformis, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus muscles.
What Is Trochanteric Bursitis?
Bursitis simply means inflammation of a bursa. Trochanteric bursitis is often referred to as greater trochanteric pain syndrome. However, the two are not the same, as GTPS describes tenderness and pain along the greater trochanteric area without inflammation and bursitis is defined by the presence of inflammation.
What Causes Trochanteric Bursitis?
Sometimes bursitis is idiopathic, meaning the exact cause isn’t known, but most of the time the inflammation is attributed to one of the following causes:
* a traumatic injury caused by a fall, slip, sport-related accident, occupational accident, or auto accident
* a previous hip injury that didn’t completely heal or formed a great deal of scar tissue
* external compression of the bursa from wearing heavy tool belts or prolonged periods of immobility
* internal compression from strain and sprain injuries to the surrounding muscles, ligaments, or tendons
* hip joint overuse, misuse, or repetitive use during work, leisure, exercise, or sport activities
* posture and gait disturbances from arthritis, scoliosis, overpronation, or leg length discrepancy
* muscular weakness or imbalance of the muscles inserting at the greater trochanter
* a bone spur on the greater trochanter can irritate and inflame the trochanteric bursa
* iliotibial band syndrome may cause friction that irritates and inflames the trochanteric bursa
* having a history of hip replacement or surgery increases the risk of developing trochanteric bursitis
Bursitis can also be the result of an infection. While a systemic infection may affect the bursa, the source of infection is more often localized. This occurs when a traumatic injury causes an open wound on the hip near the trochanteric bursa and the area becomes infected. If the infection extends into bursa sac, it‘s called septic bursitis.
What Are The Symptoms Of Trochanteric Bursitis?
* localized swelling, redness, pain, warmth, and tenderness
* the pain may worsen during squatting, running, climbing, walking, and jumping motions.
* the pain may worsen when laying on the affected side of the hip and cause difficulty sleeping at night
* the pain may radiate into the buttocks and down the outside of the thigh
Strengthening Exercises
These Hip Exercises are ideal to build strength and flexibility.
Massage Treatment
These Hip Massage Techniques are of great value in pain relief; circulation stimulation; dispersing blood and fluid accumulations; swelling reduction; and relaxing muscle spasms, especially when used alongside the Sinew Therapeutics liniments and soaks.
ACUTE STAGE SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
This stage is characterized by swelling, redness, pain, and possibly a local sensation of heat, indicating inflammation. If coolness makes your pain feel better, then the Acute Stage Treatment is recommended.
ACUTE STAGE SYMPTOMS:
The acute stage starts the moment an injury occurs and lasts until the swelling and inflammation are gone. The swelling is the result of the blockage of blood, tissue fluids and circulation in the hip because their normal movement has been disrupted by the force of the injury. Just like cars back up behind a traffic jam, causing congestion, exhaust and overheating; blood and fluids back up behind the injured hip, causing pain, inflammation, lumps and swelling.
The sensation of heat is due to the warming action of the blood and fluids overheating in the injured hip as they back up and accumulate. Stiffness and decreased mobility are due to spasms in tendons and ligaments that have contracted reflexively beyond their normal range from the impact of the injury.
As ligaments and tendons stretch and tear, blood from ruptured blood vessels becomes trapped in the local tissues. As the trapped blood clots up, it sticks the tissues together creating adhesions. Adhesions cause pain, inflammation and restricted movement because the layers of tissue that used to slide smoothly across one another now adhere and snap which interferes with normal functioning. It is essential to break up clotted blood as quickly as possible to prevent adhesions and scar tissue from forming.
During the acute stage it is very important to restore normal circulation to the hip, break up clotted blood and stagnant fluids, reduce swelling, and reduce the redness and heat associated with inflammation. By restoring the flow of blood, fluids, and circulation in the hip, then pain is relieved, damaged tissues can regenerate with healthy functional tissue, and the hip can strengthen and regain it's mobility.
ACUTE STAGE TREATMENT:
1. Apply the Sinew Herbal Ice on your hip to reduce redness, swelling, and inflammation while dispersing accumulated blood and fluids to help restore normal circulation to the hip. This first-aid treatment is used in place of ice to significantly speed up the healing process. It reduces the swelling and inflammation more effectively than ice, allowing you to more quickly regain range of motion. Acute Sinew Liniment can be used in-between applications.
Ice is not recommended because it does not help repair damaged tissues and keeps everything in the injured area frozen, causing the stagnation of blood and fluids and the contraction of muscles, tendons and ligaments. In Chinese sports medicine ice is not used and is considered a culprit in injuries that donít heal well.
2. Massage your hip with Acute Sinew Liniment to relieve pain, reduce swelling and inflammation, break up clotted blood and stagnant fluids, and stimulate circulation of blood and fluids to help cells quickly repair damaged tissues. Sinew Herbal Ice can be used in-between applications.
3. The Sinew Sports Massage Oil is recommended for use before and after exercise, sports and strenuous activity. It warms and stimulates your muscles, increases circulation and relieves tightness, hence improving your performance and helping to prevent injury.
CHRONIC STAGE SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
This stage begins once the swelling and inflammation are gone, but you still feel pain, stiffness, weakness, and/or sensitivity in cold and damp weather. If heat makes your pain feel better, then the Chronic Stage Treatment is recommended.
CHRONIC STAGE SYMPTOMS:
The chronic stage begins once the swelling and inflammation are gone, but you still feel aching pain and stiffness. This is because there are still accumulations of stagnant blood and fluids in your hip that are blocking circulation and blood supply to damaged tissues, creating residual pain, stiffness and weakness. You may actually feel hard nodules like sand in the tissue, indicating accumulation, calcification, and adhesions, which all cause pain, stiffness, and joint instability.
Your hip may feel more sensitive to the cold and ache in cold and damp weather due to impaired circulation. These symptoms are often the result of failure to treat the injury properly from the outset and overicing.
Increasing circulation and blood supply to the damaged tissues is very important in treating chronic injuries because tendons and ligaments do not have an extensive direct supply of blood. That is why chronic injuries can be slow to heal. Increasing local circulation also prevents cold and dampness from penetrating the injured area, preventing pain and stiffness.
During the chronic stage it is very important to break up remaining accumulations of blood and fluids, and increase circulation and blood supply to the damaged tissues. By increasing circulation and blood flow in the hip, then pain and stiffness is relieved, and the damaged tissues can strengthen to restore stability.
CHRONIC STAGE TREATMENT:
1. Massage your hip with Chronic Sinew Liniment to relieve pain and stiffness, strongly stimulate circulation and blood flow to damaged tissues, and promote the healing of overstretched tendons and ligaments. The Sinew Relaxing Soak and/or the Sinew Warming Soak can be used in-between applications.
2. Soak your hip with the Sinew Relaxing Soak to relax muscles and tendons that are in spasm, ease joint pain and stiffness, and improve range of motion. The Sinew Relaxing Soak is particularly useful if you feel spasms in your hip. The soak can be used by saturating a towel in the liquid and applying it to your hip. Chronic Sinew Liniment and/or the Sinew Warming Soak can be used in-between applications.
3. Soak your hip with the Sinew Warming Soak to ease joint pain, increase range of motion, and strongly increase local circulation to drive coldness and dampness out of damaged tissues. The Sinew Warming Soak is particularly useful if your hip is more painful and sensitive to cold or hurts more in cold weather. The soak can be used by saturating a towel in the liquid and applying it to your hip. Chronic Sinew Liniment and/or the Sinew Relaxing Soak can be used in-between applications.
4. The Sinew Sports Massage Oil is recommended for use before and after exercise, sports and strenuous activity. It warms and stimulates your muscles, increases circulation and relieves tightness, hence improving your performance and helping to prevent injury.







