While a posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) knee injury occurs far less often than an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), both can produce knee instability, pain, and swelling.

Anatomy As It Relates To The Posterior Cruciate Ligament
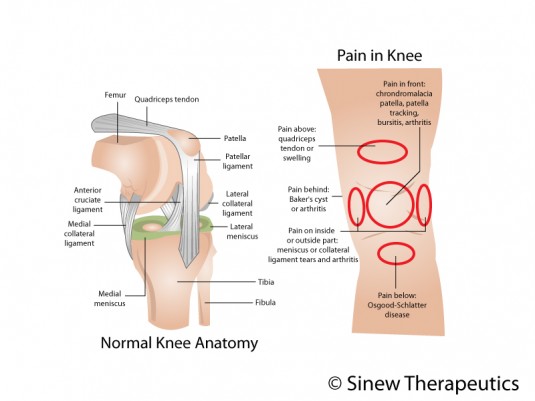
The knee joint is formed where the femur (thighbone) and the tibia (shinbone) meet. The kneecap sits in front of the joint. The joint bones are held in place by ligaments. Ligaments are tough bands of connective tissue attaching bone to bone. The posterior cruciate ligament is one of four main ligaments found in the knee. The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments make a cross at the center of the knee, acting like strong ropes to unite the bones, control the back and forth knee motions, and stabilize the knee. The posterior cruciate ligament specifically prevents the shinbone from moving too far backwards. Since it’s stronger than its anterior counterpart, it injured less often and usually takes a substantial force to sustain an injury.
What Is A Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury?
Injured ligaments are medically classified as sprains, meaning a stretching, tearing, or rupturing of the ligament. Sprains are graded on a severity scale.
Grade I - the posterior cruciate ligament is only mildly damaged. There is stretching of the ligament, but the knee joint is still stable.
Grade II - the posterior cruciate ligament is stretched to the point it becomes abnormally loose, has a partial tear, or suffers several tiny partial micro-tears. The knee joint isn’t as stable as it should be.
Grade III - the posterior cruciate ligament suffers a complete tear or rupture. The knee joint is highly unstable.
What Causes A Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury?
PCL injuries are most often attributed to a direct trauma just below the knee. There are four main causes of this type of trauma:
1. An auto accident where the knee is bent and the shinbone strikes the interior of the vehicle, such as the dashboard.
2. A fall where the knee is bent knee and the foot is pointed down, such as during sports or a misstep off a curb. The shinbone will strike the ground and move too far backward.
3. The posterior cruciate ligament can be stretched or torn if the foot is planted and the person is hit on the knee from the side, such as during a football tackle.
4. Any action that causes hyperextension of the knee.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury?
* mild to moderate pain with a grade one or two injury and moderate to severe pain with a grade three injury
* usually a rapid onset of pain tenderness, swelling, heat, and redness immediately following more severe injuries
* pain may be more intense when the knee is used to jump, run, climb, kneel, or squat
* range of motion limitations that may result in a limp or difficulty walking unassisted
* the knee may feel unstable, too loose, or as if it will give away during an activity
* localized bruising
Key Points
* a posterior cruciate ligament injury often occurs alongside damage to one of the other main ligaments, bone, or cartilage. If so, the symptoms may be more noticeable due to the coexisting injury of the other structure.
* unlike the classic symptom of an ACL injury, a posterior cruciate ligament injury usually doesn’t produce an audible pop at the time of the injury.
* posterior cruciate ligament tears are most often grade 2 sprains (partial tears) rather than complete tears or ruptures.
* when the affected knee is bent past a 90 degree angle, the knee might appear to slide backwards too far.
Strengthening Exercises
These Torn PCL Ligament Exercises are ideal to build strength and flexibility.
Massage Treatment
These Torn PCL Ligament Massage Techniques are of great value in pain relief; circulation stimulation; dispersing blood and fluid accumulations; swelling reduction; and relaxing muscle spasms, especially when used alongside the Sinew Therapeutics liniments and soaks.
ACUTE STAGE SYMPTOMS & TREATMENT
This stage is characterized by swelling, redness, pain, and possibly a local sensation of heat, indicating inflammation. If coolness makes your pain feel better, then the Acute Stage Treatment is recommended.
Acute Stage Symptoms:
The acute stage starts the moment an injury occurs and lasts until the swelling and inflammation are gone. The swelling is the result of the blockage of blood, tissue fluids and circulation in the knee because their normal movement has been disrupted by the force of the injury. Just like cars back up behind a traffic jam, causing congestion, exhaust and overheating; blood and fluids back up behind the injured knee, causing pain, inflammation, lumps and swelling.
The sensation of heat is due to the warming action of the blood and fluids overheating in the injured knee as they back up and accumulate. Stiffness and decreased mobility are due to spasms in tendons and ligaments that have contracted reflexively beyond their normal range from the impact of the injury.
As ligaments and tendons stretch and tear, blood from ruptured blood vessels becomes trapped in the local tissues. As the trapped blood clots up, it sticks the tissues together creating adhesions. Adhesions cause pain, inflammation and restricted movement because the layers of tissue that used to slide smoothly across one another now adhere and snap which interferes with normal functioning. It is essential to break up clotted blood as quickly as possible to prevent adhesions and scar tissue from forming.
During the acute stage it is very important to reduce swelling, reduce the redness and heat associated with inflammation, and break up clotted blood and stagnant fluids that are blocking circulation and blood supply to damaged tissues. By restoring the flow of blood, fluids, and circulation in the knee, then pain is relieved, damaged tissues can regenerate with healthy functional tissue, and the knee can strengthen and regain it's mobility.
Acute Stage Treatment:
1. Apply the Sinew Herbal Ice on your knee to reduce redness, swelling, and inflammation while dispersing accumulated blood and fluids to help restore normal circulation to the knee. This first-aid treatment is used in place of ice to significantly speed up the healing process. It reduces the swelling and inflammation more effectively than ice, allowing you to more quickly regain range of motion. Acute Sinew Liniment can be used in-between applications.
Ice is not recommended because it does not help repair damaged tissues and keeps everything in the injured area frozen, causing the stagnation of blood and fluids and the contraction of muscles, tendons and ligaments. In Chinese sports medicine ice is not used and is considered a culprit in injuries that donít heal well.
2. Massage your knee with Acute Sinew Liniment to relieve pain, reduce swelling and inflammation, break up clotted blood and stagnant fluids, and stimulate circulation of blood and fluids to help cells quickly repair damaged tissues. Sinew Herbal Ice can be used in-between applications.
3. The Sinew Sports Massage Oil is recommended for use before and after exercise, sports and strenuous activity. It warms and stimulates your muscles, increases circulation and relieves tightness, hence improving your performance and helping to prevent injury.
CHRONIC STAGE SYMPTOMS & TREATMENT
This stage begins once the swelling and inflammation are gone, but you still feel pain, stiffness, weakness, and/or sensitivity in cold and damp weather. If heat makes your pain feel better, then the Chronic Stage Treatment is recommended.
Chronic Stage Symptoms:
The chronic stage begins once the swelling and inflammation are gone, but you still feel aching pain and stiffness. This is because there are still accumulations of stagnant blood and fluids in the knee that are blocking circulation and blood supply to damaged tissues, creating residual pain, stiffness and weakness. You may actually feel hard nodules like sand in the tissue, indicating accumulation, calcification, and adhesions, which all cause pain, stiffness, and joint instability.
Your knee may feel more sensitive to the cold and ache in cold and damp weather due to impaired circulation. When you move your knee you may hear a clicking or popping sound from the tendons and ligaments slipping very slightly in and out of their natural alignment indicating weakness and joint instability, causing chronic pain and a cycle of reinjury. These symptoms are often the result of failure to treat the injury properly from the outset and overicing.
Increasing circulation and blood supply to the damaged tissues is very important in treating chronic injuries because tendons and ligaments do not have an extensive direct supply of blood. That is why chronic injuries can be slow to heal. Increasing local circulation also prevents cold and dampness from penetrating the injured area, preventing pain and stiffness.
During the chronic stage it is very important to break up remaining accumulations of blood and fluids, and increase circulation and blood supply to the damaged tissues. By increasing circulation and blood flow in the knee, then pain and stiffness is relieved, and the tendons and ligaments can strengthen to restore stability.
Chronic Stage Treatment:
1. Massage your knee with Chronic Sinew Liniment to relieve pain and stiffness, strongly stimulate circulation and blood flow to damaged tissues, and promote the healing of overstretched tendons and ligaments. Sinew Injury Poultice and/or the Sinew Warming Soak can be used in-between applications.
2. Apply the Sinew Injury Poultice on your knee to relieve residual pain and stiffness, significantly stimulate circulation and blood flow to damaged tissues, and further promote the healing of overstretched tendons and ligaments. The Sinew Injury Poultice is particularly useful if your knee is more painful in cold and damp weather. Chronic Sinew Liniment and/or the Sinew Warming Soak can be used in-between applications.
3. Soak your knee with the Sinew Warming Soak to ease joint pain, increase range of motion, and strongly increase local circulation to drive coldness and dampness out of damaged tissues. The Sinew Warming Soak is particularly useful if your knee is more painful and sensitive to cold or hurts more in cold weather. The soak can be used by saturating a towel in the liquid and applying it to your knee. Chronic Sinew Liniment and/or the Sinew Injury Poultice can be used in-between applications.
4. The Sinew Sports Massage Oil is recommended for use before and after exercise, sports and strenuous activity. It warms and stimulates your muscles, increases circulation and relieves tightness, hence improving your performance and helping to prevent injury.







